Defying Expectations: NASA’s Chandra Uncovers a Quasar’s Surprising Galactic Impact
Updated: 2024-03-31 18:47:18
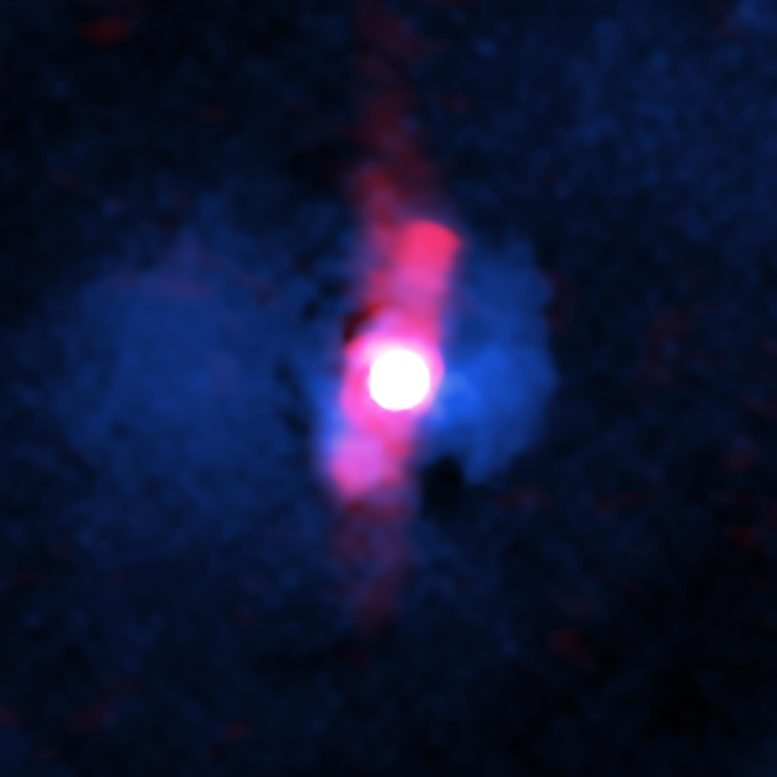 Research reveals the quasar H1821+643, despite its intense activity, has a minimal effect on its host galaxy, overturning expectations about the role of quasars. Astronomers...
Research reveals the quasar H1821+643, despite its intense activity, has a minimal effect on its host galaxy, overturning expectations about the role of quasars. Astronomers...
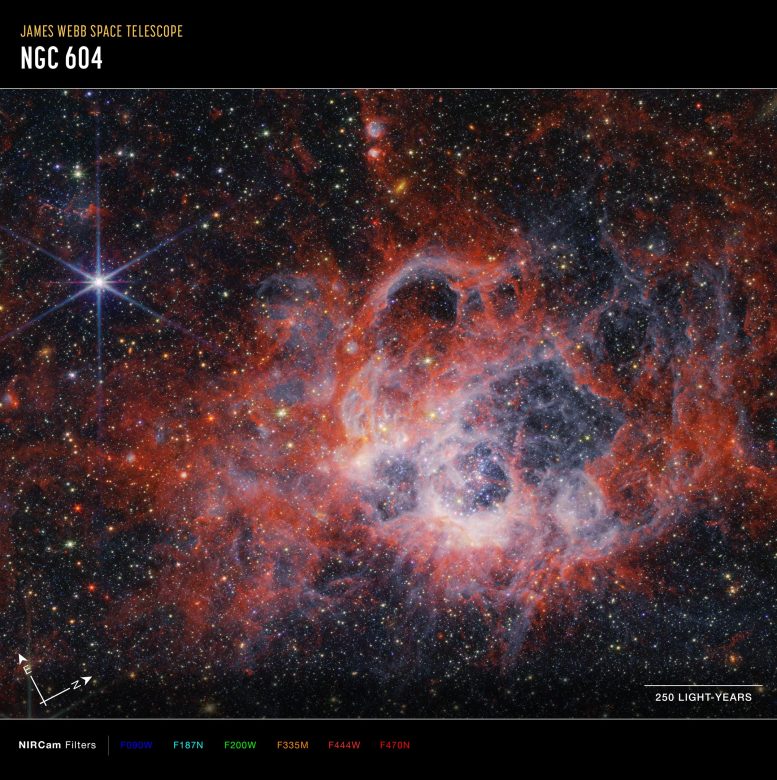 Unique Opportunity To Study High Concentration of Massive, Young Stars Nearby In the astronomy field, the term “nearby” is quite relative. Neighboring galaxies to our...
Unique Opportunity To Study High Concentration of Massive, Young Stars Nearby In the astronomy field, the term “nearby” is quite relative. Neighboring galaxies to our...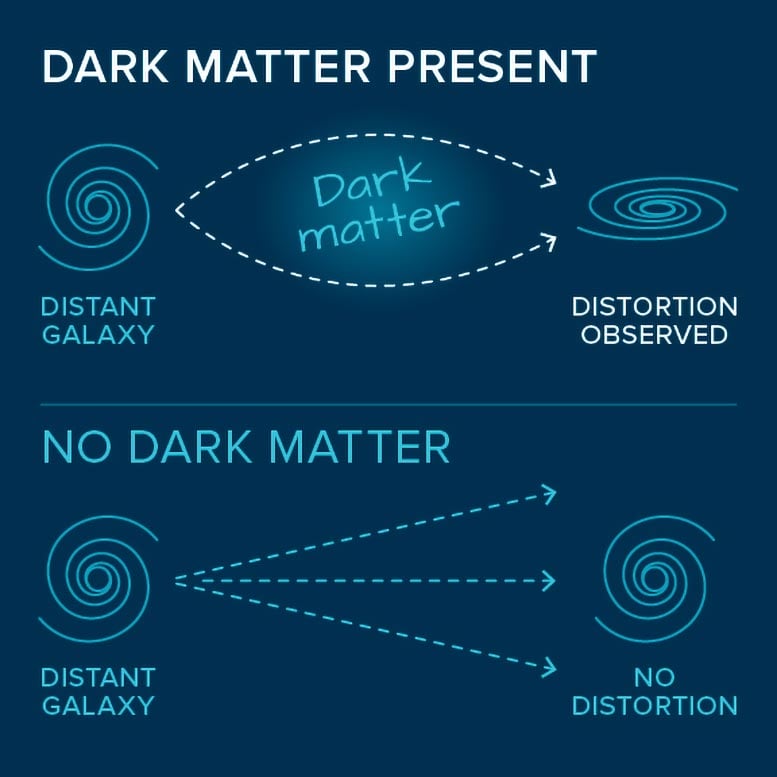 What Are Dark Matter and Dark Energy? There’s something amiss in the cosmos. Mysterious influences seem to be stretching the universe apart and clumping stuff...
What Are Dark Matter and Dark Energy? There’s something amiss in the cosmos. Mysterious influences seem to be stretching the universe apart and clumping stuff... Scientists from Massey University in New Zealand, the University of Mainz in Germany, Sorbonne University in France, and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB)...
Scientists from Massey University in New Zealand, the University of Mainz in Germany, Sorbonne University in France, and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB)...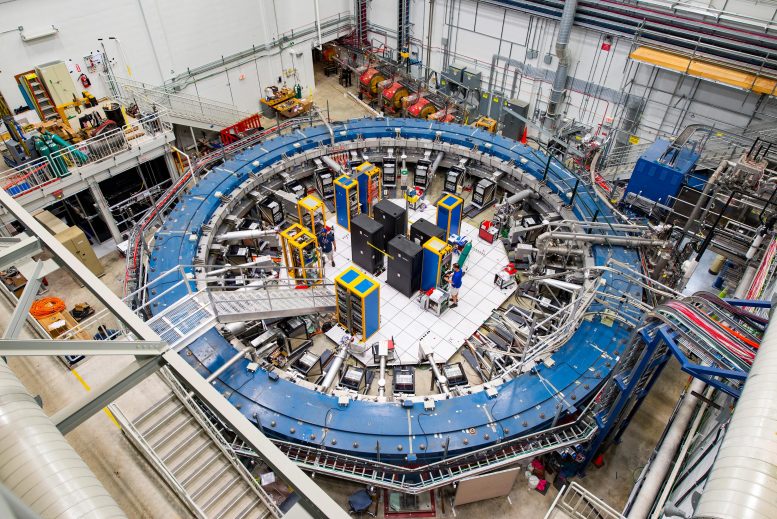 The researchers identified the origin of discrepancies in recent predictions of the muon’s magnetic moment. Their findings could contribute to the investigation of dark matter...
The researchers identified the origin of discrepancies in recent predictions of the muon’s magnetic moment. Their findings could contribute to the investigation of dark matter...